Our Team
Meet the members of the Check Valve Design Senior Project team

Alec Der Matoian
Alec will be graduating this Spring 2020 in Mechanical Engineering with a concentration in mechatronics. Alec’s project focuses included seal and assembly interfacing research, CAD modeling, and project management

Skylar Tusting
Skylar will be graduating this Spring 2020 in Mechanical Engineering, and is an incoming Design Engineer at Chevron. Skylar’s focuses on the project included analysis via CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) and interpretation of test data to drive design changes

Jessica Dent
Jessica is a 4th year Mechanical Engineering undergraduate, and will be completing her studies in Spring of 2021. Jess worked extensively on spring design & analysis, CAD modeling, and design manufacturing plans
Acknowledgements
Our team would like to recognize and thank our project sponsors and points of contact at Zurn Wilkins: Brian Yale, Reuben Westmoreland, and Chris Corral. Brian, Reuben, and Chris have been amazing sponsors to work with, as well as reliable sources of engineering consultation and advice throughout the project. We would also like to recognize Sarah Harding, senior project advisor, and Peter Schuster, senior project coordinator, for their consistent work in supporting this year’s senior project teams. Without our sponsor’s constant support and our advisor’s willingness to adapt quickly given the impact of COVID-19, this project would not have been possible.
~ Thank You ~
Our Project Videos
Introduction Video
This video provides a brief introduction and background to our project. Jessica Dent talks through the anatomy of a double check valve, the design approach and final design our team adopted, and a thank you to our sponsors and project advisor.
Engineering Video
This video provides a more comprehensive look into the engineering work that went into creating our team’s final design. Each member of the team shares talking points covering engineering specifications and requirements, design methodology, assembly and manufacturing, testing, and simulation.
Check Valve Design - Digital Poster
Problem Statement
Zurn Wilkins is requesting a new check valve design that uses mechanical advantage and fluid dynamic principles to reduce pressure loss comparative to their existing products. This design must meet industry standards for water supply backflow prevention.
Engineering Specifications
The project’s final design must satisfy the following:
- Reduction of pressure loss
- Ability to hold pressure differential (backflow prevention)
- Mechanically driven
- Meet industry standards/requirements (ASME 1015, USC FCCCHR, etc.)
Design Concept
Reasons for Selecting the Double Disk:
- Disks dynamically reduce aspect ratio of valve poppet relative to flow
- Utilizes a less constricting frame geometry, compared to traditional inline check valves
- Design can be integrated (with slight modifications) into the existing 350 XL design envelope
Other Design Considerations:
- Torsion springs and seals can be easily removed and replaced during servicing and maintenance of the check valves
- The valve assembly can be easily scaled into a double check configuration with the addition of a valve spacer
- Special seal grooves and glands can be implemented to accept industry-standard o-rings and seal gaskets to prevent backflow
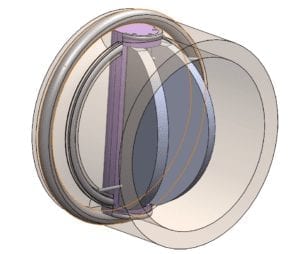
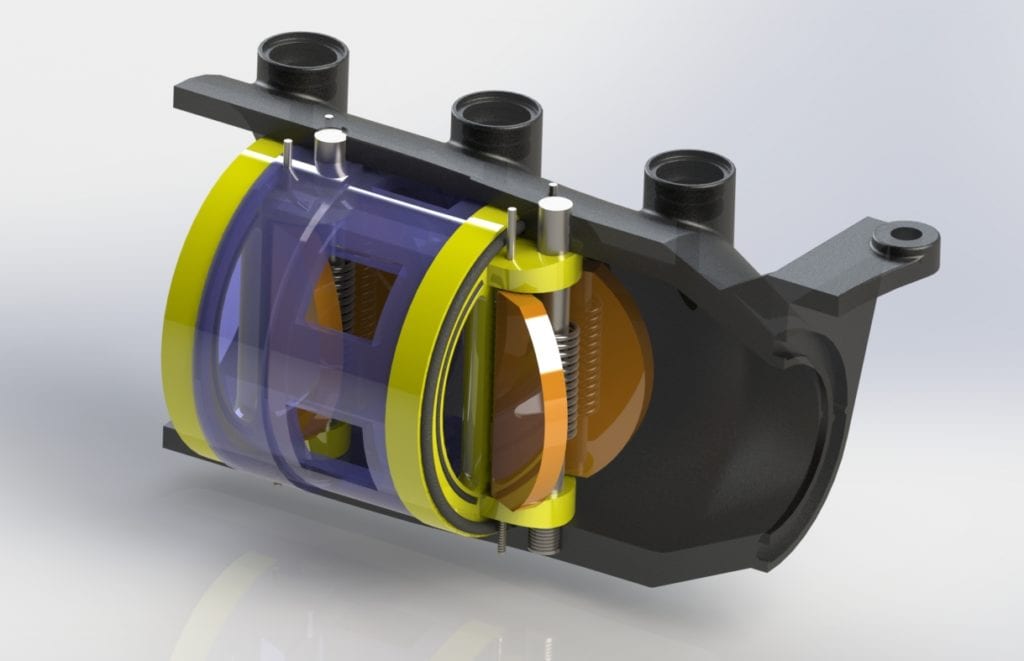
Double Disk check valve can be scaled to fit within the 350 XL housing as a double check assembly
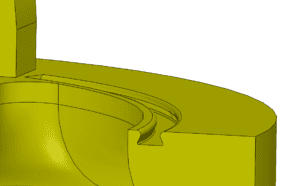
Special seal glands (dovetail) and grooves are used to ensure appropriate sealing is achieved on interfacing surfaces

Rendered CAD model of assembled (single) check valve
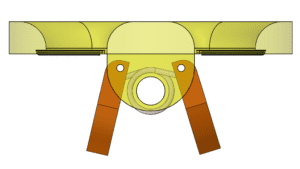
Top view of the check assembly in the open state
The detailed CAD models of each individual component of the valve assembly allowed for 3D-printed prototype parts to easily fit within the 350 XL housing for testing purposes. Accurate modeling also allowed for reliable CFD results to predict experimental testing data.
CFD Results
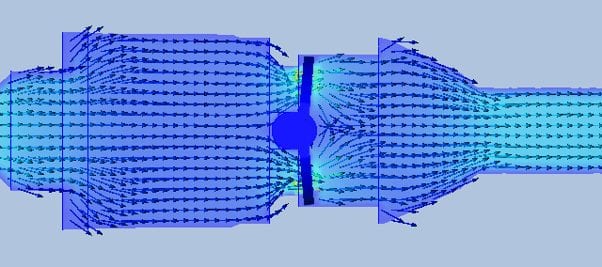
This rendered velocity field allows our team to predict fluid movement within the valve, and preemptively eliminate any obstructive geometry, if possible
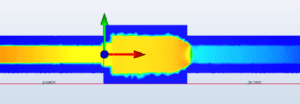
Simulating the pressure gradient of the test bench setup provides our team with an easy method to verify that our simulated results match real-world results within a respectable degree of error
CFD results have acted as a “sanity check” and predictive tool for our team’s design testing. Understanding how streamlines and path lines are generally formed within the valve can also influence early design modification for improved prototype performance.
Project Sponsor

Zurn Wilkins - Paso Robles, CA
Our team thanks our sponsors, Brian Yale, Reuben Westmoreland, and Chris Corral for their generous help throughout the duration of this project
Prototyping Process



Rapid Prototyping and Assembly:
- Our team was able to utilize Zurn’s rapid prototyping facility to quickly print, assemble, and test multiple iterations of the double disk design
- High-resolution SLA printers utilized Formlabs resin with a tensile strength of 9380 psi and tensile modulus of 402 ksi
- Once printed and cured, individual parts were sanded and then assembled to be placed in the 350 XL housing for head loss testing. This material allowed for testing of the printed assembly without fear of premature material failure.
Design Testing

Test ports on the 350 XL housing allow for a pressure delta, or differential, to be easily measured across each check valve
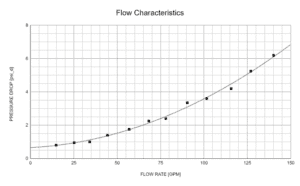
Pressure differentials are recorded at varying flow rates. Data points are collected during steady-state flow conditions. As flow rate increases, so does the pressure drop experienced by the water
Head Loss Test:
The pressure differential between each side of the check valve is measured to determine the pressure drop at differing flow rates. As flow rate increases, pressure drop generally increases as well. This test provides quantitative data to determine if a design can effectively reduce pressure loss. Pressure differentials are measured once steady state flow is achieved at flow rates ranging from 0 gpm to 160 gpm.
Backpressure Test:
The backpressure test is used to determine if the check valve is able to prevent any water from passing through the valve in a reversed-flow state. The results of this test would be qualitative, in that the valve would either pass or fail in preventing any water backflow at specific pressures and time duration.
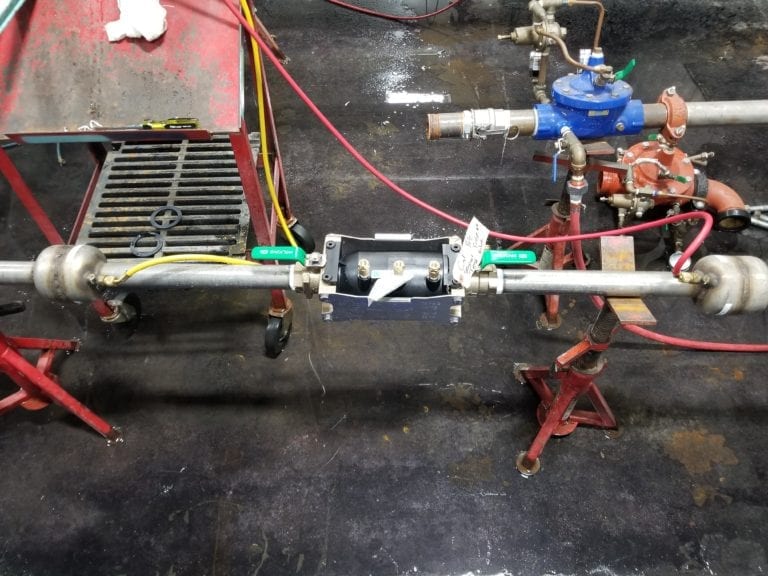
The Head Loss Test takes place within a closed-loop water flow apparatus. Water can be flown through the check valve at varying rates while measuring pressure drop
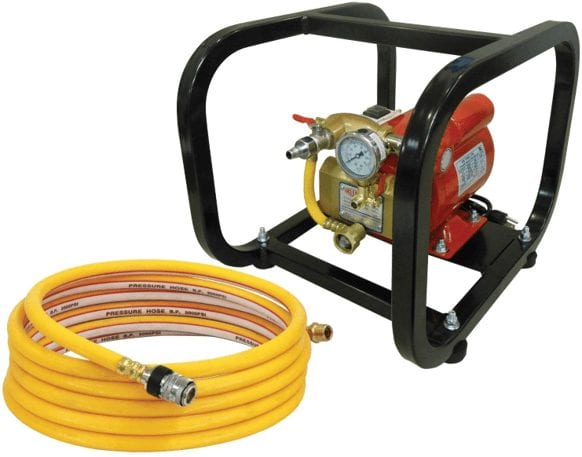

The Backpressure Test can be conducted by attempting to flow water at a specified pressure for a pre-determined amount of time into the normal discharge side of the valve. This tests the valve’s ability to prevent water backflow if flow reversal occurs
Final Design


Our final design involves slight modification to the 350 XL valve housing to allow for improvements in sealing performance and structural durability. The assembly will utilize 2 check valve sub-assemblies and a valve spacer to create a double check configuration.
Assembly Components:
- Disk Poppets (Orange)
- Valve Seat & Central Hinge (Yellow)
- Valve Spacer (Purple)
- Torsional Springs
- Hinge Pins
- Valve Seat and Poppet Seals
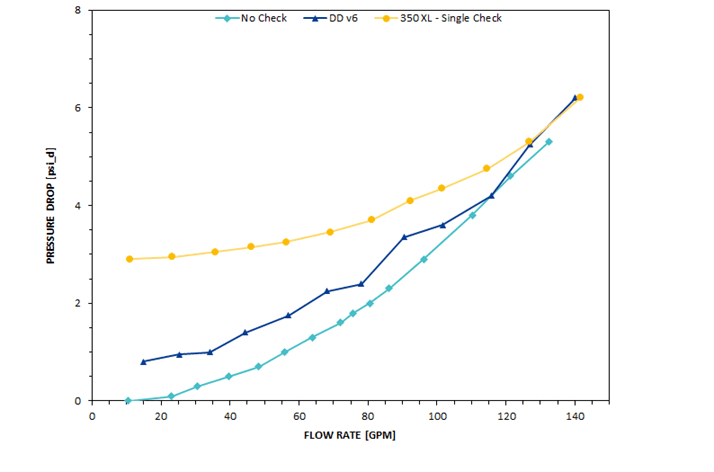
Final Test Results
Final Head Loss Test Results:
- Final Prototype (Dark Blue) head loss results indicate an improvement comparative to the inline check valve used in the Zurn 350 XL (Yellow)
- Baseline test with no check valve inside the 350 XL housing establishes the theoretical minimum head loss (Light Blue)
- Reduction in head loss of the final prototype confirms the double disk’s potential to satisfy the project’s primary objective of minimizing pressure loss
Future Application
Our team is confident that the design and data we have provided can act as a foundation for Zurn engineers to integrate the double disk check valve into a fully-functioning product intended for water supply lines. However, below are recommendations our team provides for future consideration:
- Hinge pin design improvements for enhanced sealing
- More research on fluid effects due to slotted design of valve spacer
- Improvement of torsion spring constraint within valve assembly
- Continued improvement of valve seat-to-poppet sealing interface
As the double disk design is traditionally used in applications where the strict standards of water supply backflow prevention do not apply, Zurn’s implementation of it for services involving potable and treated water would be an opportunistic and industry-leading step.

